Oral Health Benefits Explored
Article Title: Understanding Periodontitis: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Periodontitis is a serious, chronic inflammatory gum disease that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition, primarily caused by bacteria in dental plaque, can lead to significant damage if left untreated[1][2].
Common Causes
The primary cause of periodontitis is the accumulation of dental plaque, a sticky bacterial film that, if not removed through regular brushing and flossing, hardens into tartar[1][2][4]. Certain bacteria, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, play a key role by producing toxins that irritate gums[2]. Other risk factors include poor oral hygiene, smoking and tobacco use, hormonal changes, medications that reduce saliva flow, nutritional deficiencies, systemic conditions like diabetes, and a weakened immune system[2].
Symptoms
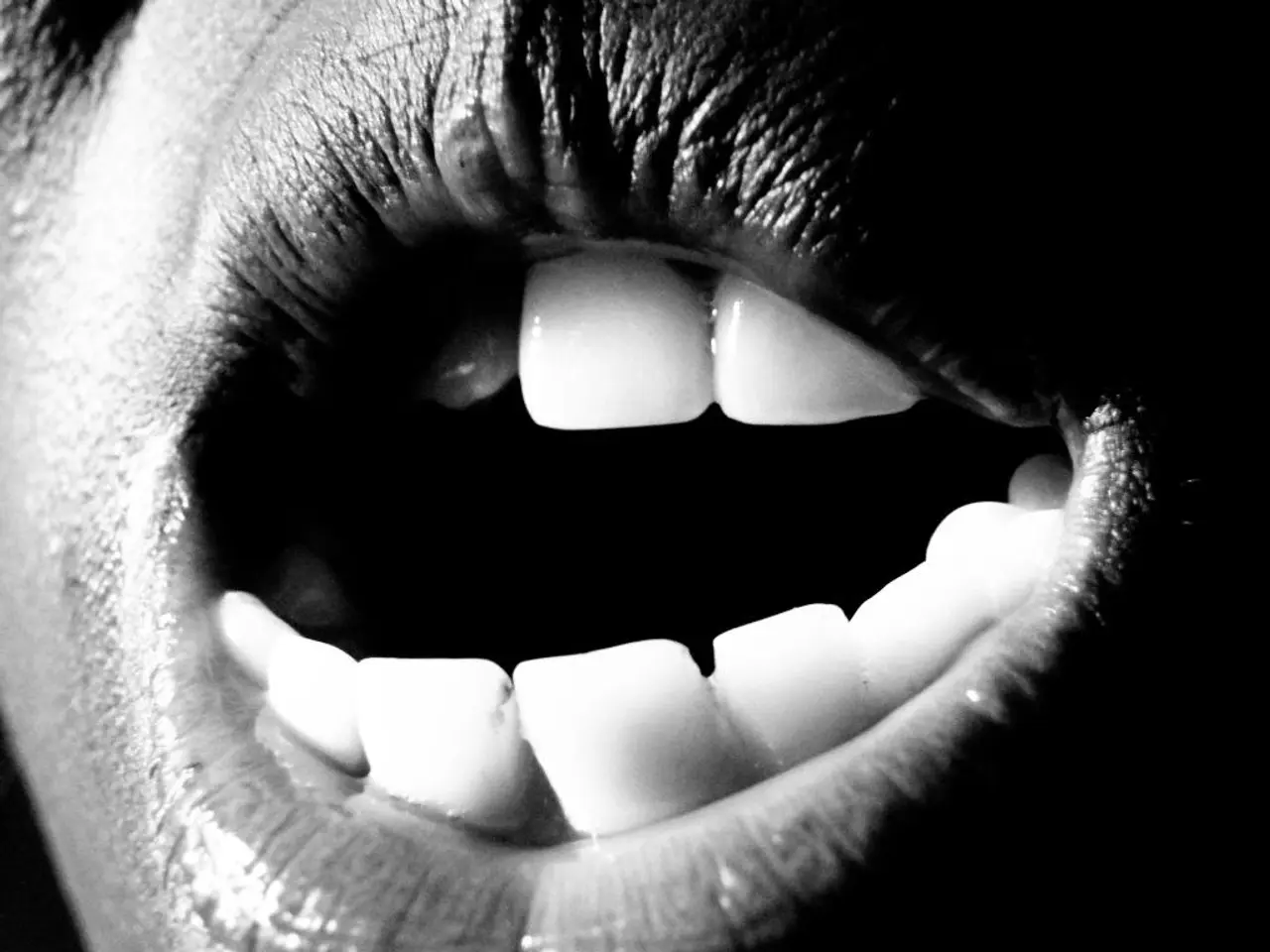
Early signs of periodontitis include red, swollen, or tender gums, gums that bleed easily, especially when brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath or bad taste in the mouth, gums pulling away from teeth (recession), forming pockets, loose or shifting teeth, pus from gums, spontaneous bleeding, and changes in bite or tooth alignment[1][3][5].
Prevention
Preventing periodontitis involves maintaining good oral hygiene through regular, thorough brushing and flossing to remove plaque and prevent tartar buildup. Regular dental visits and professional cleanings are also crucial to remove tartar that cannot be cleaned at home and monitor gum health[1][2]. Quitting smoking, managing systemic health conditions, and ensuring a balanced nutrition are also essential for preventing periodontitis[2].
Treatment
Treatment for periodontitis typically involves professional deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline[1][2]. Antibiotics or antimicrobial agents may be used to control bacterial infection. In advanced cases, procedures like flap surgery or bone grafts may be necessary to repair damaged tissues[1][3]. Lifestyle changes and maintenance, including continued careful oral hygiene and dental follow-up, are crucial for preventing recurrence[1][2].
Damage caused by periodontitis is often irreversible, emphasising the importance of prevention and early detection through regular dental care[1].
Additional Information
- Black tea has been found to kill bacteria that cause caries and gum inflammation[6].
- In pregnant women, undetected periodontitis can lead to premature or even miscarriage[7].
- Poor oral hygiene, improper diet, and a weak immune system are common causes of inflammatory gum disease[8].
- Semi-annual dental check-ups can help detect gum inflammation early and initiate appropriate treatment[8].
- Improved oral hygiene, warm sage and chamomile tea, or myrrh tinctures can alleviate symptoms of gum inflammation[8].
- Smoking weakens gum attachment and the immune system, increasing the risk of gum inflammation by five times compared to non-smokers[8].
- Tartar formation, gum swelling, inflammation, and recession from teeth create pockets, an ideal breeding ground for bacteria[9].
- Bacteria from periodontitis can enter the bloodstream and the entire human body, triggering other diseases such as joint inflammation, heart disease, diabetes, or asthma[9].
- A balanced oral flora fights pathogens and is responsible for initial digestion processes[10].
- Gum inflammation, referred to as gingivitis, can develop into chronic periodontitis, one of the ten most common diseases, affecting at least half of those over 40[11].
- Brushing teeth at least twice a day, cleaning interdental spaces regularly with dental floss or an interdental brush, and cleaning the gum line are important for maintaining healthy gums[12].
- Periodontitis is the main cause of tooth loss in adults[13].
- Drinking plenty of water, chewing sugar-free gum, and eating regularly can stimulate saliva production, which coats and hardens the teeth[14].
- The human mouth contains approximately 700 different microorganisms[15].
- Bad breath, sensitive teeth with hot or cold food, and root caries may indicate periodontitis[16].
Economic and social policy should consider the implications of periodontitis, a serious gum disease, on public health and healthcare costs. The prevention of periodontitis, primarily achieved through good oral hygiene practices, also aligns with efforts in science and research promoting health-and-wellness.