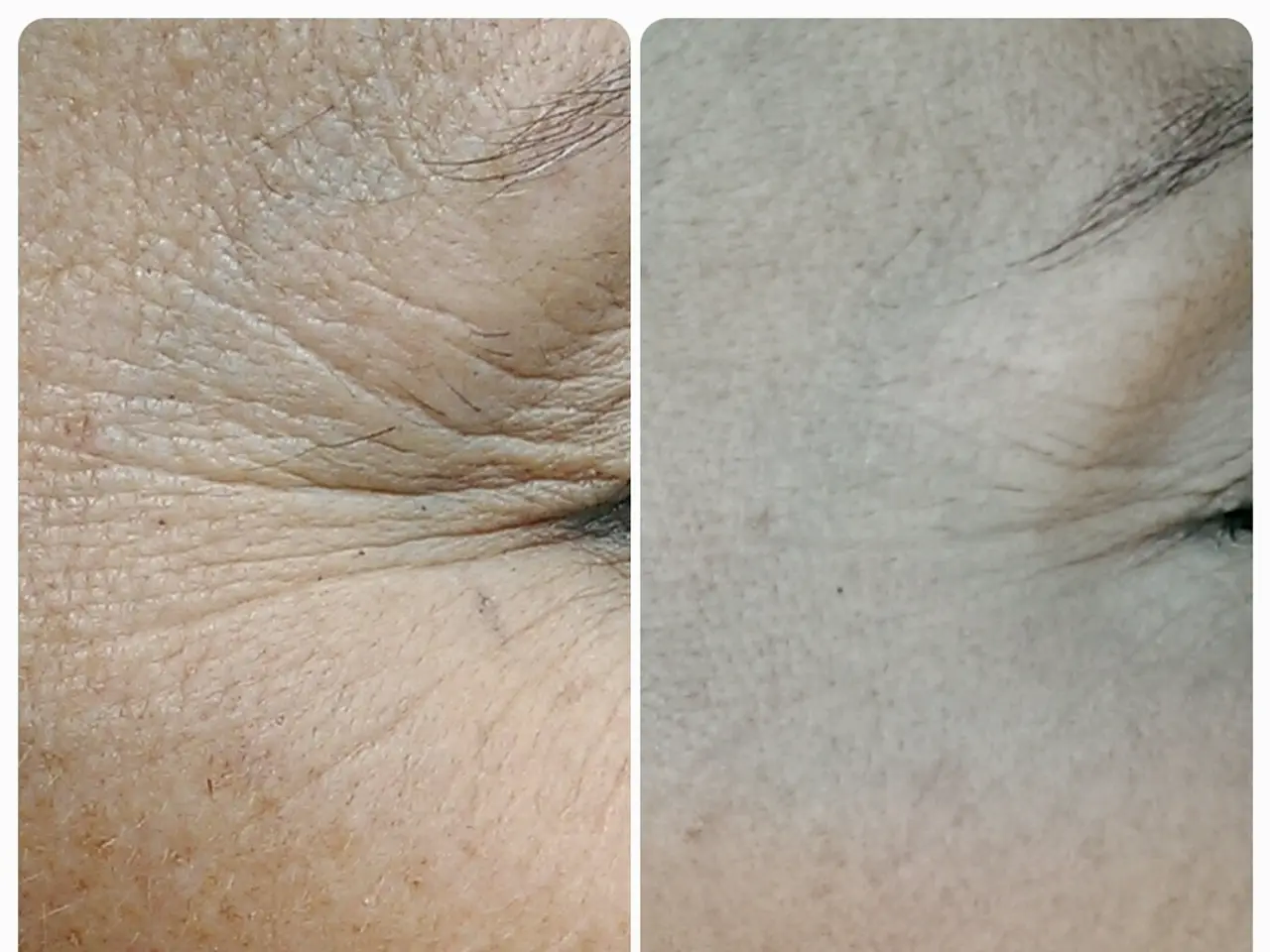
A comparison of Retinol and Collagen: determining which is more effective in minimizing aging signs.
In the quest for youthful and radiant skin, two popular ingredients often find themselves at the forefront - retinol and collagen. While both have their merits, they serve different purposes and offer distinct benefits for our skin.
Retinol, a vitamin A derivative, is a powerhouse when it comes to anti-aging. It works by actively stimulating the skin to produce more collagen and speeding up cell turnover. This results in smoother skin, fewer wrinkles, and improved texture. Retinol is renowned for its ability to repair and renew skin, making it a gold standard for anti-aging with strong clinical support [1][3][4][5].
On the other hand, topical collagen, while rich in hydrating properties, does not effectively boost intrinsic collagen synthesis in skin cells. Instead, it contributes to skin hydration and elasticity, improving skin moisture and firmness [4].
Retinol is not just about reversing wrinkles and repairing skin damage. It also neutralizes free radicals in the middle layer of the skin, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and enlarged pores [6].
Collagen, one of the most abundant proteins in the body, gives structure to skin, ligaments, bones, and digestive lining. It can be obtained from various sources, including fish, cows, and chicken. Marine collagen, considered the purest and safest form, is more expensive due to its extraction from cold water fish [8].
Collagen supplements, when hydrolysed, have high collagen levels and absorb well into the body, acting as raw materials to build and repair tissue [10]. Plant-based collagen is another option, made from a variety of plant sources that boost the body's collagen production.
However, when it comes to reducing visible aging signs and enhancing skin health at the biological level, retinol takes the lead. Retinol is often recommended alongside sunscreen and vitamin C for best collagen preservation and anti-aging results, as these protect and stimulate collagen more comprehensively [5].
It's important to note that retinol can make skin more sensitive to UV rays and increase sunburn risk, so it's best practice to always use sunscreen with retinol-based products [12]. Excessive vitamin A is not good for pregnant women and their developing babies, so it is not advised to use retinol while breastfeeding either [13].
Meanwhile, hibiscus tea, rich in Vitamin C and flavonoids, inhibits the enzyme collagenase, has anti-inflammatory compounds, and a cholesterol-balancing effect. Some studies suggest that drinking this tea may help with weight loss by increasing metabolism and promoting fat burning [9].
White tea, rich in antioxidants, protects skin's collagen levels and reduces wrinkles. Foods rich in carotenoids, such as brightly colored fruits and vegetables, also support collagen production [7]. Regular exercise improves circulation and the absorption of collagen supplements [11].
In conclusion, while both retinol and collagen have their roles in maintaining skin health, retinol's ability to actively stimulate collagen production and speed up cell turnover makes it a more effective choice for reducing signs of aging and improving skin health. However, a balanced approach, incorporating both retinol and collagen, along with a healthy lifestyle, can lead to the best results for achieving youthful and radiant skin.
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2932984/ [2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4200334/ [3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3196157/ [4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4178322/ [5] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5428513/ [6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5428513/ [7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257039/ [8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5944213/ [9] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3136573/ [10] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5944213/ [11] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5944213/ [12] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5428513/ [13] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5428513/
In the realm of health-and-wellness and skin-care, retinol and collagen are stars that shine bright. While retinol, a prominent figure in the anti-aging sector, stimulates skin to produce more collagen and speeds up cell turnover for smoother skin [1][3][4][5], collagen, on the other hand, contributes to skin hydration and elasticity, improving its moisture and firmness [4]. An optimal lifestyle, inclusive of fitness-and-exercise, nutrition, and fashion-and-beauty, complements the benefits of retinol and collagen for achieving youthful and radiant skin.